We explain what Polyhedra are in geometry, their elements, classification, and examples. We also explain their names. Please read other MTV articles for more information. If you share it, it will be of little help to us.
What are polyhedra?
According to classical geometry, a polyhedron refers to certain three-dimensional geometric bodies with flat faces that enclose a finite volume. In other words, a polyhedron is a bounded portion of geometric space, limited by different polygons. Its name comes from the Greek word polyedron, composed of polys (many) and edra (base or face).
Their names depend on the number of faces they have, using numeral prefixes of Greek origin and the ending -aedro. For example: tetrahedrons (4 faces), pentahedrons (5 faces), hexahedrons (6 faces), and so on. In addition, many polyhedra have their own names, such as cube, prism, pyramid, etc. You must read about Keyboard once.
Elements of Polyhedra
Polyhedra are made up of the following elements:
- Faces: The flat surfaces that delimit the internal space of the polyhedron. They are two-dimensional and are closed figures composed of lines. They can also be said to be the polygons that constitute it. Among them, bases are usually distinguished, which are simply the faces on which the polyhedron rests.
- Edges: The lines that make up the body of a polyhedron, and at whose intersections the vertices appear.
- Vertices: The angles where three or more edges meet in the body of a polyhedron.
Classification of Polyhedra
Beyond naming them according to their number of faces, as explained at the beginning, polyhedra can be classified according to the shape and relationship of their faces, thus forming:
- Regular polyhedra: When all their faces are regular polygons.
- Uniform polyhedra: When all their faces are equal.
- Irregular polyhedra: When their faces are unequal.
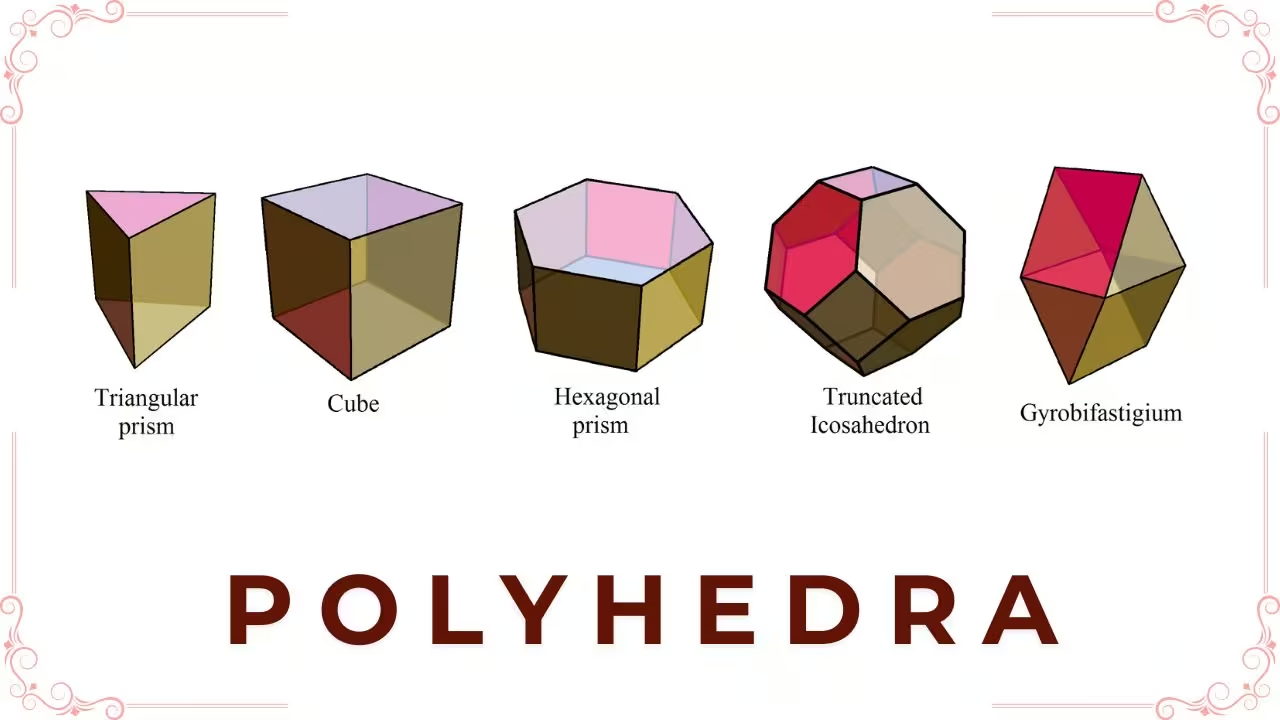
Examples of Polyhedra
The following are examples of polyhedra:
- Pyramids: Consisting of a base and several triangular faces.
- Cubes: Formed by joining six regular rectangles.
- Parallelepipeds: Constructed using two regular squares and four equal rectangles.
- Prisms: Whose faces are parallelograms, equal in number to the number of sides on their two bases.
- Dodecahedrons: Concave or convex polyhedra with twelve regular and uniform faces.
- Octahedron: Constructed by joining two pyramids at the base.
Maybe you should definitely read about Religion once.
References
- “Polyhedron” on Wikipedia.
- “What are polyhedrons?” (video) on Aula365.
- “Polyhedrons” on GeoGebra.
- “Polyhedrons” on ICT Resources.
- “Polyhedrons” on Plan Ceibal.